October is cybersecurity awareness month, a month dedicated to promoting awareness on the importance of cybersecurity. With today’s constantly evolving threat landscape, our fast-paced digital world poses unique challenges to businesses of all shapes and sizes. Cybersecurity threats such as phishing, ransomware, and data breaches are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are particularly vulnerable due to more limited resources and security measures.
This month is a great reminder for all businesses (especially SMBs) to fortify their security defenses. To help navigate this complex landscape, we’ve compiled a cybersecurity checklist to help reduce risks and alleviate total data loss.
Let’s dive in.
The SMB Cybersecurity Checklist
1. Maintain a strong password policy
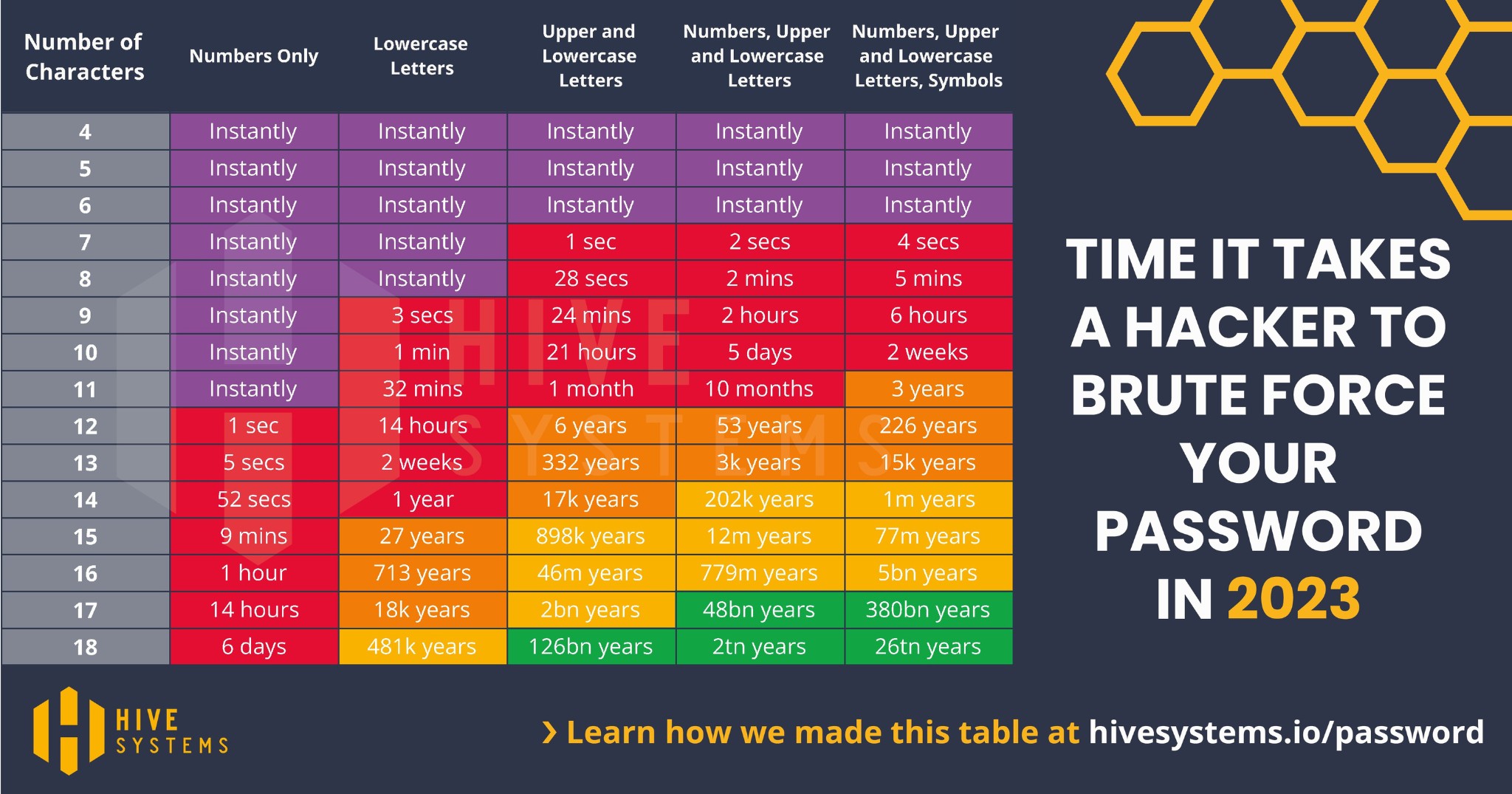
In general, the longer the password the better. Try to limit reusing passwords for different accounts and avoid using personal information, such as a birthdate, name, etc. Change your passwords regularly, and use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Ensure these passwords are securely stored and consider using a password manager.
Confident in your password? Check how long it would take a hacker to brute force your password in 2023.
2. Be on the lookout for phishing emails and phone scams.
Phishing continues to be one of the most popular attack vectors for cybercriminals. Be wary of suspicious emails, hyperlinks, and calls. Always hover over a link before you click, but when in doubt, report it.
3. Conduct an annual security assessment
Regular security assessments are crucial for knowing where your baseline currently stands each year and what can be improved. Proactively address vulnerabilities while adapting your security measures for potential evolving threats.
4. Make sure backups are up to date
Plan certain dates to perform backups or automate the process because… “You are only as good as your last backup.” Follow the 3–2–1 rule for peace of mind that important files are safe no matter what happens to your physical office or online presence.
3–2–1 rule = 3 copies on 2 different mediums, with 1 stored online
5. Enforce mandatory cybersecurity training sessions
Your employees are your first line of defense against cybercrime. Almost all modern cyber-attacks against businesses use some form of social engineering to gain access. Holding regular training sessions including the latest threat trends helps keep all employees up to date.
6. Monitor user access
It’s good practice to periodically review employee and third-party access rights to important data and resources. Ensure the right users have the right access to certain data and documents. This helps minimize the risk of insider threats and accidental data exposure.
7. Use multiple layers of security
Multifactor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection to your systems by confirming the user’s identity with other devices and platforms. By requiring employees to verify their identity using a secondary device, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, even in the event of a compromised password.
8. Have clear guidelines on data management
Create a document about data and file classification, storage, access, and disposal that all employees will follow. This not only protects your data but also helps maintain compliance with industry regulations.
9. Continually re-examine policies and procedures
Cyber threats are constantly evolving. Your policies and procedures need to evolve too. Determine various checkpoints throughout the year to ensure policies are still applicable or need to be updated.
10. Deploy endpoint security
Individual devices, such as computers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets are attractive targets for cybercriminals. Only having antivirus is not enough. Endpoint security goes beyond traditional antivirus software to provide a multi-layered defense against threats such as malware, phishing, and ransomware.
11. Regularly evaluate BYOD policies
More and more companies are moving to a hybrid work environment. It’s important to revisit BYOD policies as the organization changes (ex: remote working) to ensure devices are up to date with current business needs and security standards.
12. Update all software when updates are available
Keeping software up to date reduces vulnerabilities and security holes that hackers are looking for.
By following this comprehensive checklist, your SMB can be more confident in its ability to reduce security risks. Cybersecurity is an ongoing process. It’s important to stay vigilant and informed on the latest practices to protect what matters most to your business.
Interested in learning more? Fill out the form below and one of our representatives will be in touch with you shortly.





